AWS Availability Zones vs. AWS Edge Locations: A Comparison
AWS Availability Zones (AZs) and AWS Edge Locations are both crucial components of the AWS infrastructure, but they serve distinct purposes and have different characteristics.1
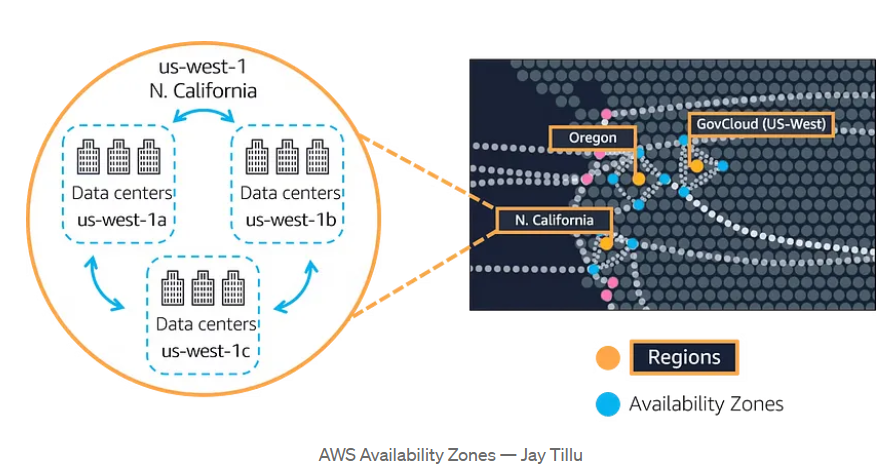
AWS Availability Zones (AZs)
- Purpose: To provide high availability and fault tolerance for applications and services within a specific AWS Region.2
- Physical Isolation: AZs are physically isolated data centers within a single Region, often separated by significant distances to minimize the impact of single-point failures.3
- Services: Host a wide range of AWS services, including compute, storage, databases, and networking.
- Focus: Primarily on infrastructure redundancy and disaster recovery.4
AWS Edge Locations
- Purpose: To deliver content and applications closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving performance.5
- Physical Distribution: Edge Locations are distributed globally, forming a vast network of points of presence (PoPs).6
- Services: Primarily used for content delivery and caching, often in conjunction with services like Amazon CloudFront.7
- Focus: On optimizing content delivery and reducing latency for end-users.8
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | AWS Availability Zones (AZs) | AWS Edge Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | High availability, fault tolerance | Content delivery, reduced latency |
| Physical Location | Isolated data centers within a Region | Distributed globally |
| Services | Wide range of AWS services | Primarily content delivery and caching |
| Focus | Infrastructure redundancy | Performance optimization |
In essence:
- AZs are about keeping your applications and data safe and available, even in the face of unexpected events.9
- Edge Locations are about delivering your content and applications to users as quickly and efficiently as possible.10
Visual Representation:
By understanding the distinctions between these two essential components of the AWS infrastructure, you can make informed decisions about how to design and deploy your applications and services to meet your specific needs for reliability, performance, and scalability.